UNIX
COMMANDS
Sno
|
Command
|
Description
|
1
|
date
|
Displays
the Date
|
2
|
cal
|
Displays
the calendar
|
3
|
pwd
|
Print
name of current/ working directory
|
4
|
cat
|
For
creating and displaying files
|
5
|
ls
|
Displays
list of files
|
6
|
chmod
|
Change
permissions
|
7
|
mkdir
|
To
create a directory
|
8
|
cd
|
To
change a directory
|
9
|
cd
..
|
To
jump back one level in directory
|
10
|
rm
|
Remove
a file
|
11
|
rmdir
|
Remove
a directory
|
12
|
cp
|
For
Copying files
|
13
|
mv
|
For
moving and renaming files
|
14
|
wc
|
Count
characters, words and lines
|
15
|
head
|
Displays
first part of file
|
16
|
tail
|
Displays
last part of file
|
17
|
grep
|
Searching
for a pattern in file
|
18
|
man
|
manual
|
19
|
telnet
|
Log
into another machine
|
20
|
touch
|
Creating
a file
|
21
|
cut
|
Used
to cut the fields to the given data base
|
22
|
dd
|
Used
to change the lower text to upper text
|
23
|
banner
|
Used
to print the text up to 10 characters
|
24
|
cowsay
|
Used
to print full text
|
25
|
ln
|
Creat
a link between old and new file
|
26
|
clear
|
Clears
the terminal content
|
27
|
bc
|
It
is used to operate all the operators
|
28
|
tty
|
Terminal
operations are done by this command
|
29
|
tput
|
Terminal
output operations are done by this command
|
30
|
gedit/nano/vi
|
These
commands are used to edit a file
|
31
|
sed
|
stream
editor for filtering and transforming text
|
32
|
toilet
|
display
large colourful characters
|
33
|
figlet
|
display
large characters
|
34
|
ps
|
report a
snapshot of the current processes.
|
Syntax:
$date
Example:
$date
Mon
Jan 6 04:40:00 EDT 2015
2. For viewing the content of a file.
3. For adding text to the existing file “ram”,
2.cal:
(Displays the calendar)
Description:
This command is used to see the calendar of any specific month or
complete year
Syntax:
$ cal
Example:
$ cal displays the current calendar.
3.Pwd
: (Print Name Of Current/Working Directory)
Description:
print name of current working directory.
Syntax:
$pwd
Example:
$pwd /home /rit
4.Cat:
(For creating and displaying files)
Description:
this command is used to create, view and concatenate files.
Syntax:
1.
$cat > filename - for creating the file
2.
$cat filename – for viewing the file content
3.
$cat <file1><file2> - for concatenating the contents of
file1 to file2.
4.$cat
>> ram - To append current file.
1.Example:
$cat> ram
Ram
Is
A
Good
Boy
(at
the end of file press ctrl+D to save the file)
2. For viewing the content of a file.
$cat
ram
ram
is
a
good
boy.
3. For adding text to the existing file “ram”,
We
do this
$cat
>>ram
with
a
nice
behavior
<control+D>
Note:-
Now see the contents of “ram” using
$cat
ram.
(display
the entire text)
4.
For concatenating of two file
Suppose
that we have another file named “sita” which looks like
$cat sita
sita
is
a
good
girl
$cat
ram sita
ram
is
a
good
boy
with
a
nice
behavior
sita
is
a
good
girl
If
we want to save the contents of two files into file name ramesh we
use the following command.
$cat
ram sita>ramesh
Now,
if we use $cat ramesh command then it displays the above contents of
ram and sita.
- Ls: (Displays list of files)Description: to list out all the files & directories available in our directory.Syntax : lsEx: lsram rit sitals r*6.Chmod: (Change permissions)Sticky bit: d r w x r w x r w x in which the first bit is allocated to directory (d) / file (-) the next 3 bits are for USER and the next 3 bits are for GROUP and the next 3 bits are for OTHERSDescription:chmod Set the permission on a file or a directory.
Syntax:
chmod [options] <who> <opcode> < permission>
<filename>
Options:
-R Recursively updates permissions within a directory
structure.
Who:
u user
g
group
o
other
a
all
Opcode:
+ add permission.
-
remove permission.
Permission:
r
read
w
write
x
execute
Eg:
chmod a +rwx public-file
adds
permissions of read write and execute to all.
Eg:
chmod go -wx my-file
removes
write and execute to group and others.
-
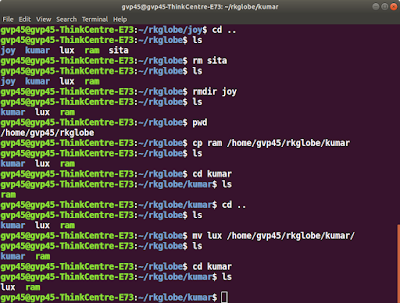
Mkdir: (To create a directory)
Description:
use this command to create a directory.
$mkdir<directory
name>
Ex:
mkdir abc
-
Cd: (change directory)
Description:
use cd to change directory. Use pwd to see in what directory you are.
Ex:
$cd abc
$pwd
/home/rit/abc.
-
Cd ..
Description:
to jump back one level in directories.
Syntax:
$ cd ..
/home/rit/abc
Cd
..
/home/rit
10)rm
(removes a file)
Description:
use rm to remove a file from your directory.
Syntax:
$rm <file name>
$rm
sita
11)rmdir
(remove a directory)
Description:
use this command to remove a directory but the directory should be
empty (no files).
Syntax:
$rmdir <directory name>
Ex:
$rmdir abc.
12)Cp
(for copying files)
Description:
use cp copy files to another file or directory.
Syntax:
$cp <source> <destination>
Ex:
$cp ram xy
13)Mv:
(for moving and renaming)
Description
: use mv for changing the name of the file.
Syntax:
mv <old file name> <new file name> for renaming
Mv
<file name > <directory name> for moving to directory
14)Wc
: (word count)
Description:
use this command to count the number of characters(-c), words(-w) and
lines(-l) in a file.
Syntax:
wc <file name>
Ex
: wc zzz
4
9 41 zzz
wc
–c <file name>
Displays
no. of characters in a file
Wc
–w <file name>
Displays
no. of words in a file
Wc
–l <file name>
Displays
no. of lines in a file
15)Head:
(display the first part of a file)
Description:
use this command to see the head of the file.
Syntax:
head <file name> displays the first 10 lines of a file
Ex:
head -2 zzz
16)Tail:
(displays the last part of a file)
Description:
use this command to see the last part of a file.
Syntax:
tail<file name> for the last 10 lines of file
Ex:
tail -2 zzz
Nic
Behavior
Description:
stream editor for filtering and transforming text
Syntax:
sed -n “3,6p” <filename>
where
n = no of lines
p=
no assigned to page line
18)Grep:
(searching for a pattern in a file)
Description:
the grep program searches a file/ files for lines that have a certain
pattern.
Syntax:
grep pattern files
Example:
grep is zzz xy
19)Man
(manual)
Description:
this command acts as a manual
Syntax:
man <command name>
Ex:
man cat
20)telnet:
Description:
telnet is used to log in another machine
Syntax:
telnet ip address
Ex:
telnet 10.10.13.32
21)touch
: Creating a file.
Description: The touch command simply creates an empty file. The below touch command creates a new file in the current directory.
Syntax: touch new_file.txt
Description: The touch command simply creates an empty file. The below touch command creates a new file in the current directory.
Syntax: touch new_file.txt
Ex:
touch ram.txt
22)cut:
Used to cut the fields to the given data base
Description:
The cut is used to cut the fields of a given file Syntax:
cut –d”=” –f 1,3 play
Ex:
create a file play with fields name=play=age
23)dd:
Used to change the lower text to upper text
Description:
Used to change the text lower to upper and vice versa
Syntax:
dd if=ram of =ravi conv=ucase
Ex:
input file is ram with ram is a boy
output
file is ravi with RAM IS A BOY
24)banner:
Used to print the text up to 10 characters
Description:
Used to print the text with only 10 characters including spaces
Syntax:
banner <text>
Ex:
banner ram is a boy
banner
“ram is a boy”
25)cowsay:
Used to print full text
Description:
Used to print the text with all the characters including spaces
Syntax:
cowsay <text>
26)ln:
Creat a link between old and new file
Description:
Used to create a link between old file and new file Syntax:
ln <oldfile name> <newfile name>
Ex:
ln ram sita
27)clear:
clear the terminal content
Description:
Used to clear the terminal
Syntax:
clear
28)tty(Terminal operations are done by this command)
28)tty(Terminal operations are done by this command)
Description:
To
print the file name of the terminal connected to standard input
(keyboard) you need to use command called tty. This command is
available on Solaris, Linux, FreeBSD, and other Unixsh operating
systems. The tty utility writes the name of the terminal attached to
standard input to standard output. You can also use who or w command
to find out terminal/tty.
Syntax:
tty
Ubuntu
has 7 tty's.1-6 are command line only, 7 runs your X
session (your normal desktop).
To
access them, use this keyboard shortcut:
Ctrl + Alt + F1
(changing F1 to
F1-F6 to access the terminal that you want)
To
get back to your X session (the normal desktop),
Ctrl + Alt + F7
29)tput(Terminal
output operations are done by this command)
Description:
This command is used to change the terminal colour
Syntax:
Examples:
tput
setaf 3 ; echo “ this is the colour”
tput
setaf 5 ; echo “ this is the colour”
30)
gedit/nano/vi
Description:
these commands are used to a edit and modify a file.
Syntax:
gedit/nano/vi <filename>
31)figlet
Description:
these commands are used to print the text in different style.
Syntax:
figlet <type text here>
32) toilet
Description: display large colourful characters
Syntax:
toilet <type text here>































No comments:
Post a Comment